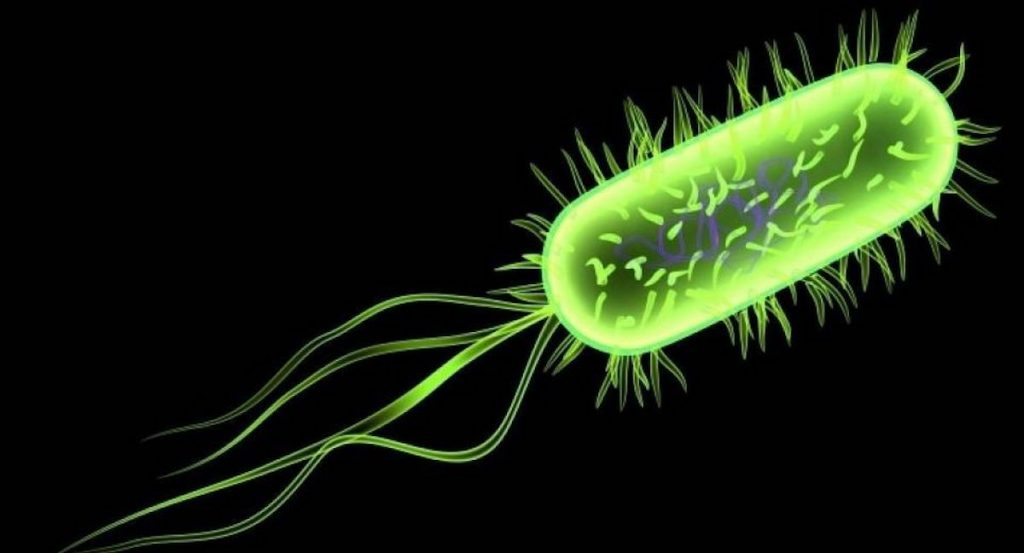
The activity of cancer drugs changes depending on the types of microbes living in the gut, according to a UCL-led study into how nematode worms and their microbes process drugs and nutrients.
The discovery illustrates the possible advantage of influencing gut bacteria and diet to improve cancer treatment and the value of understanding why the usefulness of drugs varies between people. The study, published today in Cell and funded by Wellcome, the Royal Society and Medical Research Council, reports a brand new high throughput screening technique that unravels the complicated connection between a host organism, their guts microorganisms and drug activity. The effectiveness of colorectal cancer therapies varies significantly between individuals. We wanted to know if this might be due to microbes changing how a body processes the drugs. We have developed a rigorous system which might be used for pre clinical screening of drug interactions in the context of host and microbe, or for creating microorganisms for drug delivery that could revolutionise solutions, described study lead, Dr Filipe Cabreiro.
We forget there are several microorganisms living in our bodies that communicate with the food and drugs we ingest. Until now, probing the connection between host, microbe and drug has proved difficult. Frequently microbes are studied in solitude, which isn’t practical, but utilizing our in vivo technique, we have had some striking insights on how drugs exercise may be bolstered or suppressed by gut microorganisms, said Dr Timothy Scott, first author. The team, regarding scientists from UCL, the European Molecular Biology Laboratory, University of Helsinki and Birkbeck, University of London, developed a brand new 3 way screen based on C.
Elegans. This worm is commonly utilized as a simple model for human metabolic process because of its evolutionary similarity to humans and its equivalent connection with microorganisms. They screened 55, 000 problems in C. Elegans by varying bacteria genes as well as the types of medications and doses. The team then utilized computational evaluation to map in great detail how a bacteria’s genetics, diet sources and chemical substances influenced the usefulness of fluoropyrimidines, a typical kind of colorectal cancer drug. Fluoropyrimidines act by preventing DNA is produced, which prevents cells from separating within an uncontrolled style, an average feature of cancer cells.
They’re commonly given in a professional drug type, and therefore it requires to be broken down by the liver to become active drug. Even though fluoropyrimidines are common cancer treatment, there’s no generally accepted dose and genetics alone don’t explain differences in patient response to the drug. The substantial screening in this study outlined two unique ways that microorganisms change drug action in worms. First of all, some bacteria strains assist to process the pro drug into an active drug type, improving drug exercise, and subsequently, the microorganisms influence the metabolism environment of the cell making it more predisposed towards drug induced cell death. The team also found that co treatments for cancer might limit treatment success if the host microbe drug interactions aren’t taken into account. For instance, they found the anti diabetic drug metformin reduces the effectiveness of fluoropyrimidines in C. Elegans by inhibiting the positive actions of microorganisms.
“We’ve highlighted a critical missing component in our understanding of how drugs really work to treat disease. We plan on investigating this area further, as identifying which microbes are responsible for drug activity in humans, and their regulation by dietary supplements, could have a dramatic impact on cancer treatment outcome,” Dr Cabreiro concluded.
More from Things Health
-
Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
Cancer of the prostate affects more than 200,000 men each year in the US alone. Worldwide statistics for prostate cancer continue to grow tremendously, and…
-
10 Addictions that Could Be Affecting Your Life
You’re out for dinner with a friend, but are you catching up with them, or spending your time on Facebook, Twitter or Instagram? Today it’s…
-
Types Of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer happens when skin cells are damaged, for instance, by overexposure to ultraviolet rays from the sun. Melanoma - the most dangerous type of…
-
Proton Therapy Cancer Treatment
Proton treatment, also called Proton beam treatment, is the most sophisticated radiotherapy currently accessible - it destroys cancer cells, but does not attack encompassing healthful…
-
7 Deadly Diseases That Afflict Black Americans
There are 7 deadly diseases that affect more black Americans than white Americans. These diseases hit harder and occur more often in the said demographic.…