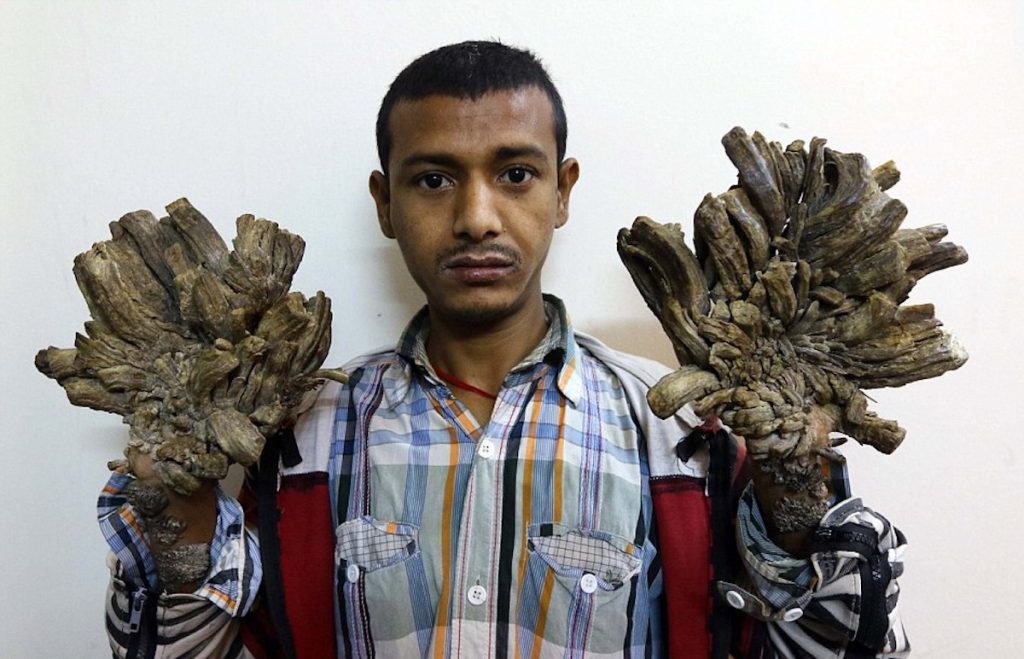
Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva, “Stone Man Syndrome”
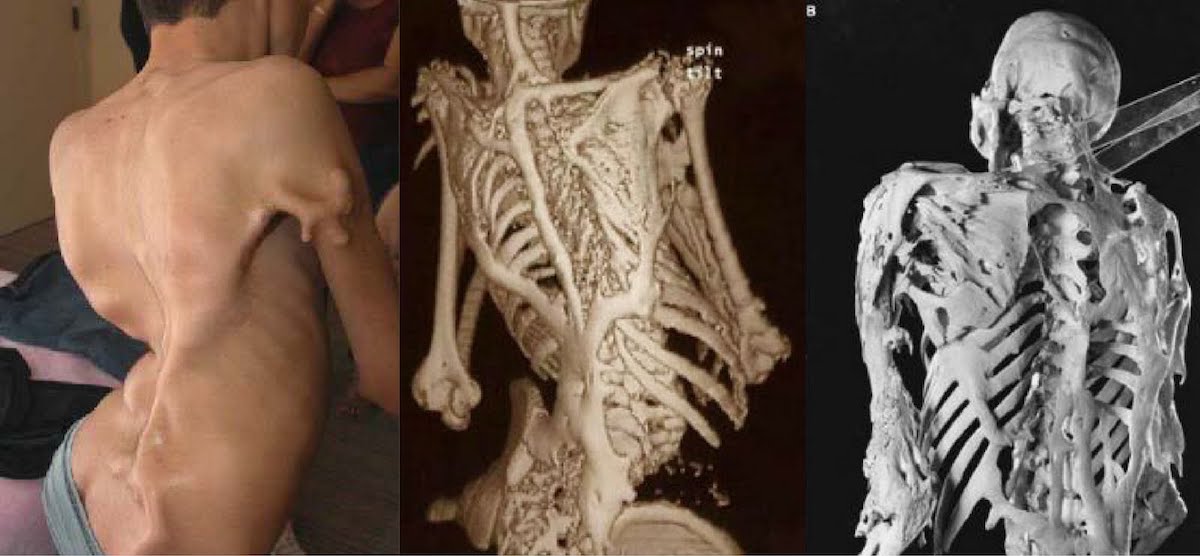
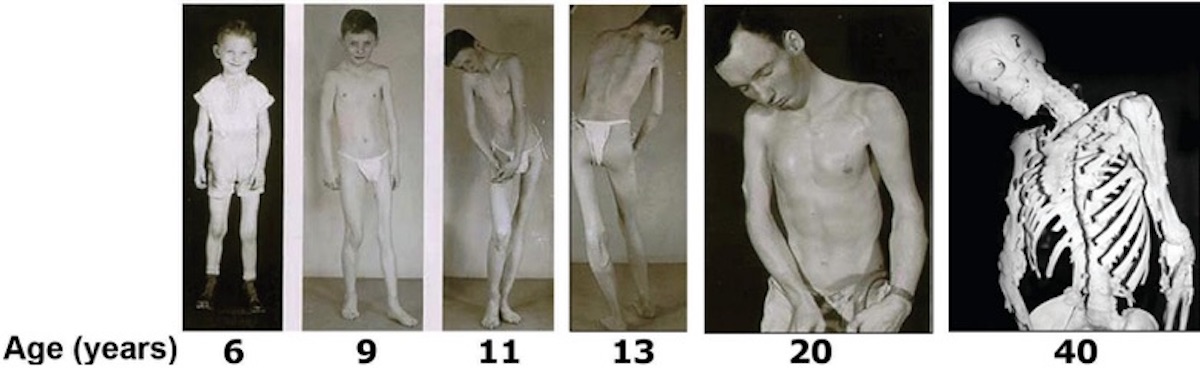
Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva, more commonly known as “Stone Man Syndrome” or FOP is a progressive genetic disorder that targets the body’s connective tissues. This disease is so rare that only one person in two million are believed to be affected by this disease with a total of 700 cases worldwide and almost 300 in the United States specifically. In those individuals with FOP, when any of the fibrous tissues such as a ligament, muscle, or tendon become damaged, they turn into bone via a process known as ossification. In no other disease or disorder does a part of one the body’s systems turn into something completely different.
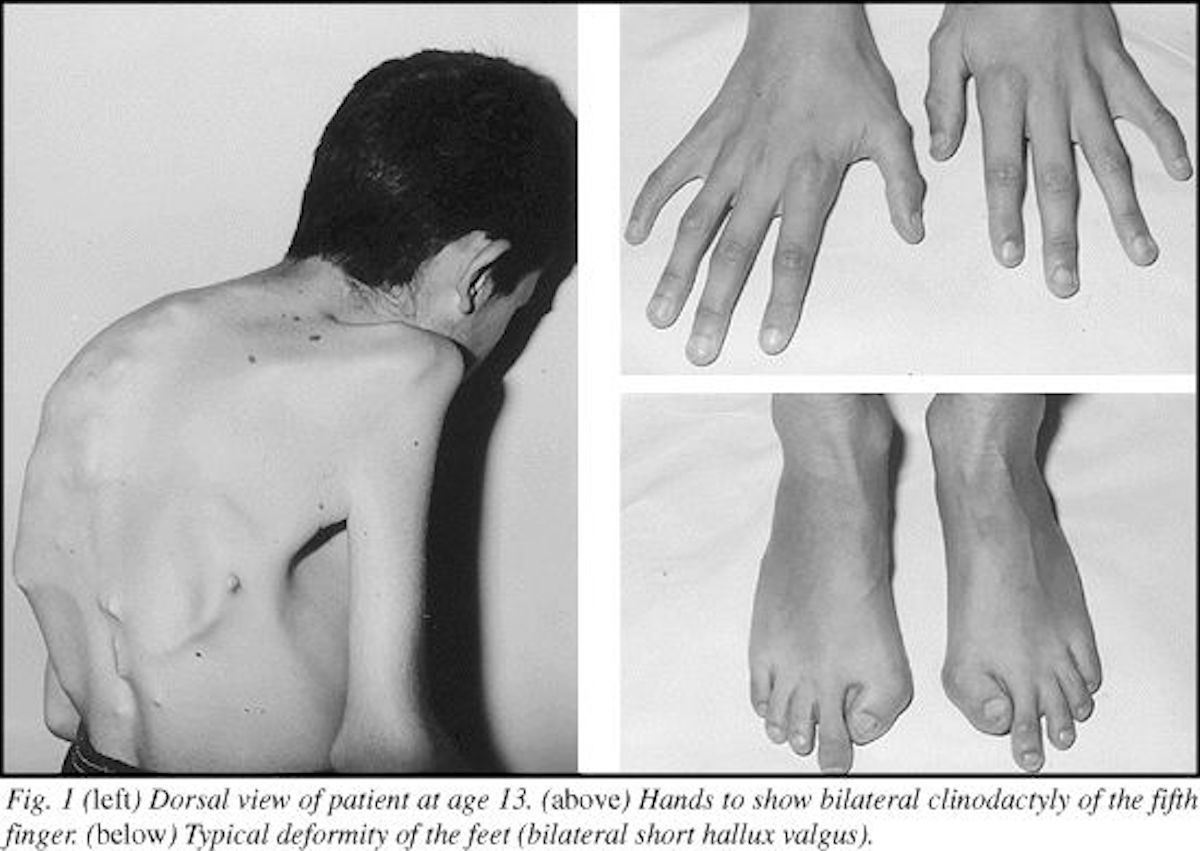
One main indicator of FOP at birth is a malformed big toe. Unfortunately, to date there has been no medical breakthroughs in the treatment of FOP. Moreover, when treatment is attempted to get rid of the bone that is formed, more bone seems to be produced in this area. The cause behind FOP is a defective ACVR1 gene. This gene’s main purpose is to allow the body to convert cartilage into bone when we are children; however, due to a strange mutation of this gene it can also cause connective tissues to turn into bone and for joints to be fused together.
More from Things Health
-
Signs and Symptoms of Liver Damage
There are a variety of different causes of liver damage. For some, it is caused by genetics, making an individual prone to it, exposure to…
-
Visual Signs of Poor Health That Should Not Be Ignored
We often think that being diagnosed with an illness such as diabetes, heart disease, stroke or cancer as something that happens out of the blue.…
-
10 Common Symptoms of Having an Anxiety Disorder
What is normal? Sometimes it is difficult to determine when getting nervous or anxious is a normal feeling, and when you might have an anxiety…
-
The Most Common Causes of Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation, Afib, is an abnormal heart rhythm, also known as an arrhythmia. Atrial fibrillation is described as rapid and irregular beating of the atrium,…
-
The Most Common Symptoms of Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia affects almost six million Americans. It is a pain disorder that influences the musculoskeletal system and alters the way that pain is processed by…