Huntington’s Disease
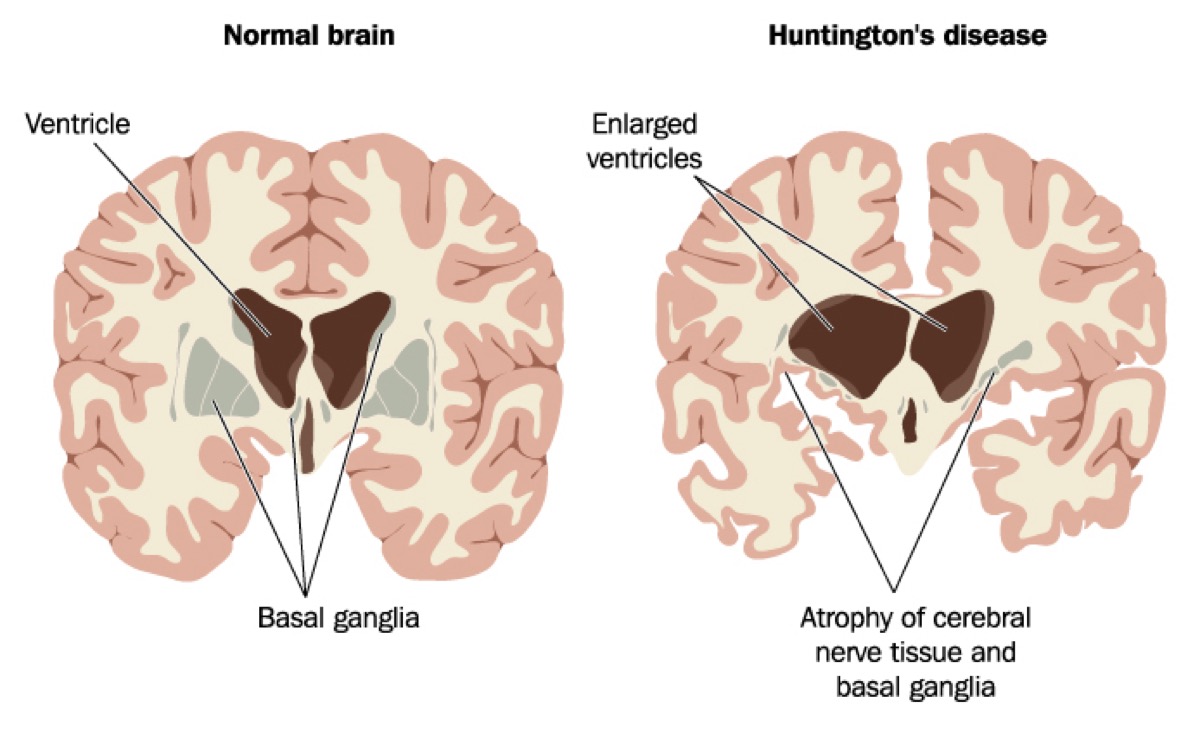
Huntington’s disease (HD) is an inherited autosomal dominant disorder that attacks nerve cells in the brain and causes cells in the central nervous system (CNS) to deteriorate. The loss of these nerve cells throughout the nervous system causes mood swings, behavioral changes, chorea—snake-like movements—and uncontrollable twitches or ticks, difficulty with locomotion, memory loss, speech impediments, and swallowing difficulties. However, there are other symptoms ranging from physiological to psychological that can develop. People with Huntington’s disease also typically have depression and are at risk of other psychiatric conditions like obsessive-compulsive disorder, bipolar disorder, and manias.
While HD can develop early in life (known as juvenile HD), there is also a type that develops during adulthood during the 30s and 40s and is very common. HD can be easily passed onto children. One parent with HD means the child has a 50% of inheriting it. This also means that those who inherit the gene will be affected by Huntington’s disease eventually.
More from Things Health
-
The Common Cold
Common cold, also known simply as a cold, is a viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract that primarily affects the nose. The throat,…
-
The 8 Most Common (And Terrible) Sleep Disorders
After a long day, there is nothing better than getting into bed for a good night’s rest. However, according to the most recent Sleep Index…
-
The Rarest Medical Conditions in the World
Having a disease that is more rare does not necessarily mean that it is associated with more severe symptoms, even though this is often how…
-
The Most Common Causes of Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation, Afib, is an abnormal heart rhythm, also known as an arrhythmia. Atrial fibrillation is described as rapid and irregular beating of the atrium,…
-
Top 6 Most Common Leukemia Symptoms
One of the most common cancers, according to the Mayo Clinic, leukemia is the “cancer of the body’s blood-forming tissues.” Leukemia attacks the body’s white…