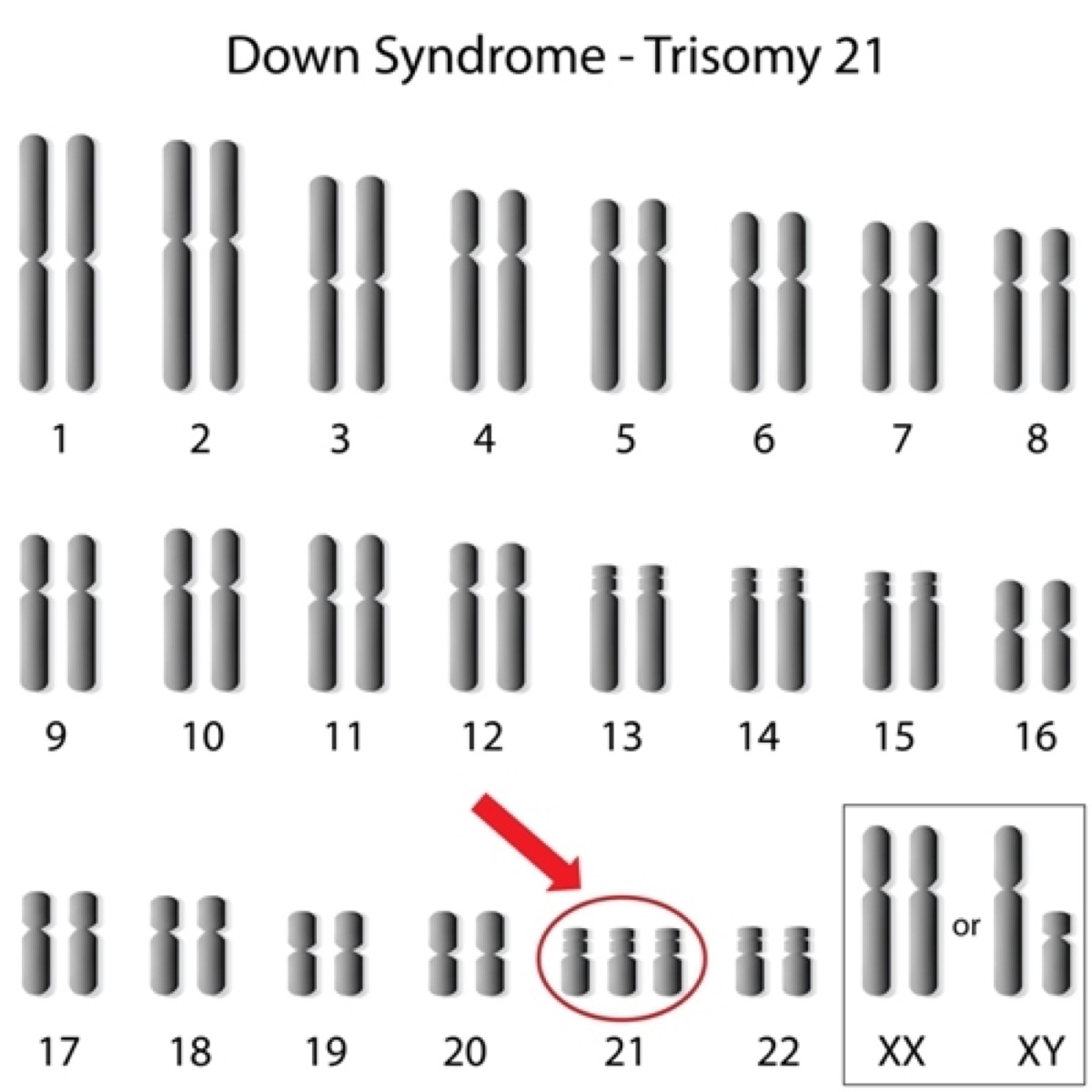
Down Syndrome
In many cases, Down syndrome is not inherited. Rather, it occurs at random during the meeting of the egg and sperm cells. The condition begins in chromosome 21. Presently, Down syndrome affects every 1 in 800-1000 infants born around the world.
Down syndrome can be diagnosed during infancy through genetic testing. A blood or skin sample is collected to check for the presence of an extra chromosome, called trisomy 21. Trisomy 21 is when there is a trio of chromosome 21 instead of two. The extra chromosome disrupts normal brain development and causes the features characteristic of Down syndrome.
The common effects include learning and speech difficulties, mental retardation, flattened facial features, and hypotonia (poor muscle tone). These individuals also have an increased risk of digestive problems, hearing loss, heart defects, and usually have hypothyroidism. Early intervention programs can help with enhancing growth and learning capabilities of individuals with Down syndrome, enabling most to live and work independently.
More from Things Health
-
The Common Cold
Common cold, also known simply as a cold, is a viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract that primarily affects the nose. The throat,…
-
The 8 Most Common (And Terrible) Sleep Disorders
After a long day, there is nothing better than getting into bed for a good night’s rest. However, according to the most recent Sleep Index…
-
The Rarest Medical Conditions in the World
Having a disease that is more rare does not necessarily mean that it is associated with more severe symptoms, even though this is often how…
-
The Most Common Causes of Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation, Afib, is an abnormal heart rhythm, also known as an arrhythmia. Atrial fibrillation is described as rapid and irregular beating of the atrium,…
-
Top 6 Most Common Leukemia Symptoms
One of the most common cancers, according to the Mayo Clinic, leukemia is the “cancer of the body’s blood-forming tissues.” Leukemia attacks the body’s white…