Confusion and Seizures
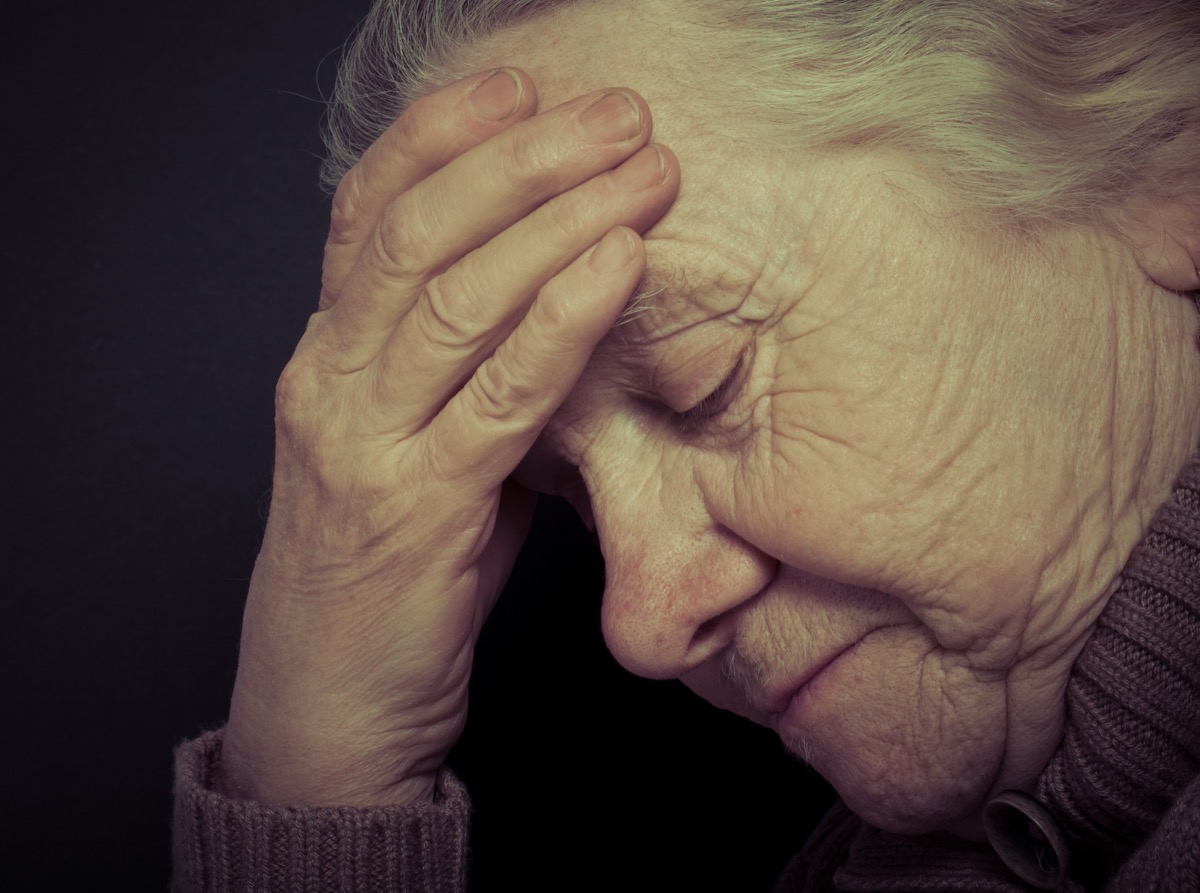

Because systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) causes inflammation within nearly every tissue of the body, it should be unsurprising that the brain can also become inflamed. When the brain is affected, it’s called cerebritis. In the event that Lupus affects the brain, patients will experience headaches, seizures, strokes, and even psychosis.
Psychosis is a mental disorder that causes a defective thought process, including frequent delusions (false beliefs), hallucinations, paranoia, and disordered behaviors and speech patterns. While this might be shocking, only 3% of lupus patients will experience psychosis as a cause of the autoimmune disease. However, while psychosis is infrequent, doctors do classify it as a classic symptom of SLE and will look for it during diagnosis.
Lupus will attack the nerve cells of the brain, too. 50% of patients will describe frequent memory loss, fatigue, brain fog, and have trouble describing thoughts. Similarly, the effect on nerve cells can cause things like seizures, drooping eyelids, ringing in the ears, vision problems, and even carpal tunnel syndrome. Children are more likely to develop neurological disorders as a symptom of Lupus than adults.
More from Things Health
-
Signs, Symptoms and Risk Factors of Lupus
Lupus, an autoimmune disorder, is a chronic condition (which means that it lasts for years) that affects approximately 1.5 million Americans. Lupus is one disease…
-
Symptoms of Gout
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by recurrent attacks of a red, tender, hot, and swollen joint. Pain typically comes on rapidly in…
-
Symptoms Of Epilepsy
Epilepsy a neurological disorder marked by sudden recurrent episodes of sensory disturbance, loss of consciousness, or convulsions, associated with abnormal electrical activity in the brain.…
-
Symptoms Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune illness, which accompanies irritation of the joints and apparent deformities. Maybe a virus, causes an attack on the synovium…
-
Symptoms Of An Ulcer
A peptic ulcer is an open sore in the top digestion tract. Both primary kinds of peptic ulcers, a gastric ulcer, which forms in the…