Causes
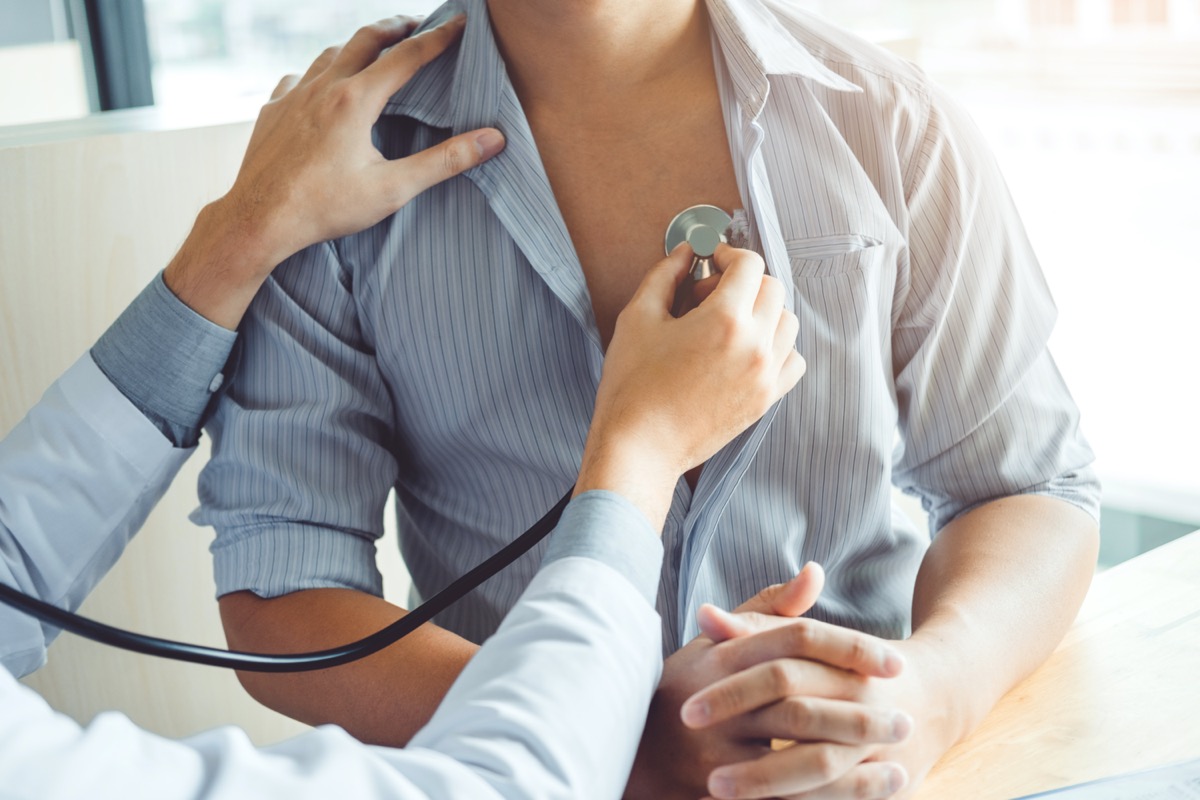
Genes and other medical conditions are known to cause pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Some conditions will change, damage, or block the blood vessels, raising your blood pressure. Pulmonary hypertension (PH), however, is when your blood pressure is raised within the pulmonary arteries. In many cases, the cells has changed—thickening and stiffening. Excess tissue may form, causing restricted blood flow.
Pulmonary hypertension is dangerous for this reason. The pulmonary artery is connected the heart’s right ventricle and the lungs. When the artery is congested, the heart must work harder to transport blood into the lungs for oxygenation, thus raising blood pressure within the lungs.
There are four known groups of common causes of PAH:
• Group 1: Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH). When the cause is unknown, it is known as idiopathic pulmonary hypertension.
• Group 2: Pulmonary hypertension from left-sided heart disease, such as aortic valve disease or mitral valve issues
• Group 3: Pulmonary hypertension from lung diseases
• Group 4: PH caused by conditions for uncertain reasons, such as metabolic disorders, tumors, conditions affecting organ systems, and blood disorders.
More from Things Health
-
The Most Common Causes of Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation, Afib, is an abnormal heart rhythm, also known as an arrhythmia. Atrial fibrillation is described as rapid and irregular beating of the atrium,…
-
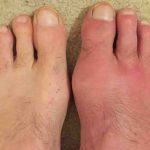
Symptoms of Gout
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by recurrent attacks of a red, tender, hot, and swollen joint. Pain typically comes on rapidly in…
-
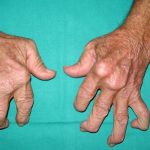
Symptoms Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune illness, which accompanies irritation of the joints and apparent deformities. Maybe a virus, causes an attack on the synovium…
-
Mindfulness And Meditation
Meditation was found to have a favorable influence on the body, brain, and spirit. Successful direction of persistent pain, reduction in blood pressure level, and…
-
Symptoms Of Epilepsy
Epilepsy a neurological disorder marked by sudden recurrent episodes of sensory disturbance, loss of consciousness, or convulsions, associated with abnormal electrical activity in the brain.…